doctor Puneeth sir may recommend surgery for a diabetic foot ulcer if there is a significant amount of dead or infected tissue surrounding the wound. Wound care specialists can clean out the ulcer to help it heal and prevent an infection from developing or worsening.
Some people with diabetes also have lower extremity arterial disease, a condition that reduces blood flow to the legs and feet. This may prevent a foot injury from getting the nutrients it needs, delaying healing.If you experience recurring or chronic ulcers in a certain areas of the foot because of poor alignment, Our orthopedic surgeons may suggest surgery to improve the position of the bones in the foot. Poor alignment occurs when the bones of the foot don’t line up evenly, resulting in the uneven distribution of body weight across the foot.
Bones bluntly identified by probing a diabetic foot ulcer can help diagnose osteomyelitis. Probing to bone was 66% sensitive and 85% specific for osteomyelitis (grade B) in a prospective study. Radiographs are of limited value in diagnosing acute osteomyelitis because radiographic changes usually lag behind clinical infection. Although plain radiographs are not sensitive to osteomyelitis, bone destruction on plain films is diagnostic of osteomyelitis. Technetium bone scans are very sensitive to osteomyelitis, but their lack of specificity limits their clinical utility. Similarly, leukocyte scans are sensitive but not specific, unable to distinguish overlying cellulitis from deeper bone infections. The combination of technetium bone scanning followed by leukocyte scintigraphy was 92.9% accurate (grade C) in diagnosing osteomyelitis in a prospective study. Gallium scanning was ineffective in diagnosing osteomyelitis of the foot pedal (grade C). Recently, magnetic resonance imaging has been further developed as a sensitive test for osteomyelitis, although it is hampered by the fact that it is unable to distinguish acute osteoarthopathy from osteomyelitis. A recent cost analysis of treating diabetic foot infections concluded that non-invasive osteomyelitis testing significantly increases treatment costs while having little impact on outcomes (grade C).
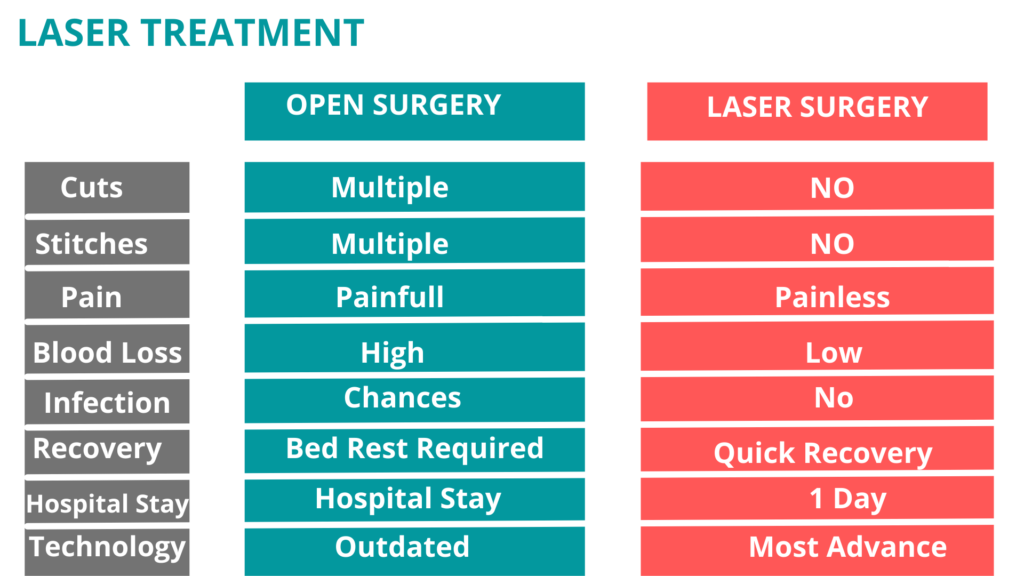
Since 85% of lower extremity amputations in diabetics are preceded by a non-healing ulcer, it is evident that prevention and healing of these ulcers is desirable. Several studies have documented the association between diabetic neuropathy and foot ulcers (Grades B and C) and the benefit of full-contact plaster cast in healing neuropathic ulcers (Grade C). Total Contact Casts are thinly padded, molded casts that are placed on the lower extremity of diabetics with uninfected neuropathic ulcers that decompress the ulcer and promote healing while maintaining the ability to walk. Therapeutic footwear, rocker sole shoes, the Carville splint, and Scotch™ casts have all been described as aids in ulcer healing and amputation prevention (Grades A and C). Recently, interest has focused on growth factors as a means of promoting ulcer healing. Human recombinant platelet growth factor (becaplermin) is commercially available and has been shown to increase the rate of ulcer healing in chronic non-healing ulcers compared to placebo (Grades A and B). Conversely, fibroblast growth factor was shown to be no more effective than placebo in promoting ulcer healing (grade B). A prospective placebo-controlled study of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor found that it promotes earlier cellulitis resolution, shorter hospital stays, and reduced parenteral antibiotic use in patients admitted with acute diabetic foot infections (Grade A). Unfortunately, neuropathic ulcer recurrence rates, once healed, can be as high as 70% over the next 5 years. In a small study of patients with severe diabetic foot infections, particularly those with evidence of ischemic vascular disease (grade C), hyperbaric oxygen therapy was shown to reduce the rate of major amputations. Other anecdotal modalities have been suggested as potential treatments for diabetic foot infection, but the lack of supporting literature limits their use.
Why Choose Angio care ?
- 25% off on Diagnostics.
- One Day Discharge
- No Paperwork hassle.
- 20000+ Successful Procedures done.
- 100% Insurance Cover.
- No Cost EMI Available
- Dedicated Care Buddy
- Free Pickup & Drop Service.
Top Vascular Specialist in Hyderabad
Removal of devitalized tissue to control infection and create an environment conducive to healing while maximizing the structural and physical integrity of the foot is the central goal of surgery in the treatment of diabetic foot infections.
Surgical procedures range from simple outpatient debridements to guillotine amputations in diabetics with life-threatening infections.
Abscesses of the foot or toes are best addressed through lateral incisions that avoid load-bearing surfaces. Diamond-shaped incisions in the plantar or dorsal surfaces are used to drain the mesh space. Unfortunately, in this area, errctious sequelae such as amputations. Amputations for diabetic foot infections should not follow the classic textbook descriptions, rather they should be limited to removing all necrotic, devitalized tissue and bone while sparing as much skin and tissue as possible. Arterial reconstructive surgery is an important adjunct to therapy and may be required to heal an amputation or non-healing ulcer, in patients with documented vascular disease. Arterial bypass surgery to the pedal vessels has reduced the incidence of lower extremity amputations for diabetic foot infections (grade C), nonetheless the percentage of amputees who are diabetic remains disproportionately high. Attempts to reduce the incidence of lower extremity amputations has shown that multi-disciplinary team management, with emphasis on preventative measures, is one of the more effective means of accomplishing this goal (grade C).
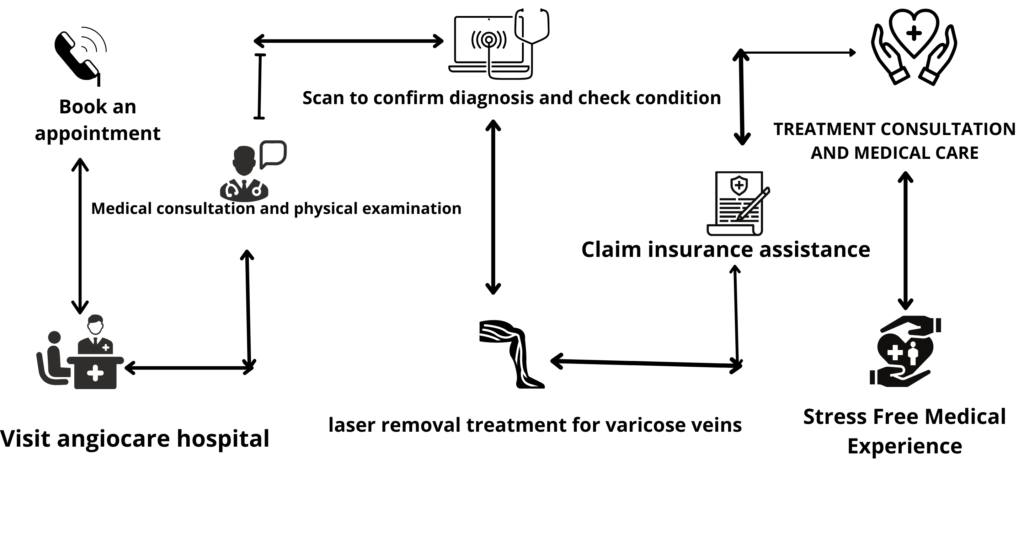
Patient Journey to Angiocare Hospital